The Differences Between PVC and XLPE Cables
December 17, 2023What is Armoured Cable
In the realm of electrical engineering, cables are classified based on their structure, material, and application. They play a crucial role in transmitting power and communication signals across various environments. One of the key categories in this classification is the armoured cable, designed for enhanced protection and durability.
Types of Armoured Cable
- Steel Wire Armoured (SWA) Cables: They are commonly known as SWA cables, an abbreviation for Steel Wire Armour. SWA cables are ideal for areas with significant drop heights and are designed to endure external mechanical forces as well as considerable tension.
Structure: Consists of steel wire or aluminum wire armor.
Application: Used in underground systems, power networks, and cable ducting. Ideal for industrial applications due to its robust nature.
- Steel Tape Armoured (STA) Cables: Commonly referred to as STA cables, short for Steel Tape Armour, these cables are well-suited for underground installation. They are capable of resisting external mechanical forces, although they are not designed to withstand substantial tensile stress.
Structure: Protected by a layer of steel tape.
Application: Suitable for indoor and underground applications, offering excellent mechanical protection.
- Aluminum Wire Armoured (AWA) Cables: Typically referred to as AWA cables, short for Aluminum Wire Armour, these cables benefit from the non-magnetic properties of Aluminium. This prevents the induction of currents in the armour from the currents flowing in the main conductor. Aluminum Wire Armour is primarily used in single-core cables.Structure: Aluminum wire armor, lighter than steel.
Application: Commonly used in power networks where mechanical stress is minimal.
Read Also: The Differences Between PVC and XLPE Cables
Difference Between Steel Wire Armoured (SWA) Cable and Steel Tape Armoured Cable (STA)
When it comes to protecting electrical cables, armoring is a critical factor that enhances their durability and functionality in various environments. Among the most commonly used types are Steel Wire Armoured (SWA) cables and Steel Tape Armoured (STA) cables. Understanding the differences between these two types of cables is essential for selecting the right cable for specific applications.
Construction:
SWA Cable: SWA cables are constructed with a layer of steel wire armor. This armor is typically made up of individual steel wires wound around the cable.
STA Cable: In contrast, STA cables are armored with steel tape. This tape is a thin strip of steel, wrapped around the cable.
Mechanical Protection
SWA Cable: The steel wire construction provides high mechanical protection. This makes SWA cables suitable for use where the cable is exposed to higher levels of mechanical stress, such as in industrial or construction environments.
STA Cable: STA cables, with their steel tape armor, offer good mechanical protection but are generally not as robust against impact or crushing forces compared to SWA cables. They are more suitable for environments where mechanical stresses are moderate.
Flexibility
SWA Cable: The individual wires in SWA cables offer more flexibility compared to the solid steel tape in STA cables. This makes them easier to bend and install in complex routing areas.
STA Cable: STA cables are less flexible due to the nature of the steel tape armor. They are more suited for straight runs or where minimal bending is required.
Read Also: Top 10 Electrical Safety Tips Every Homeowner Should Know
Weight and Handling
SWA Cable: The use of steel wires makes SWA cables heavier and more challenging to handle and transport.
STA Cable: STA cables are generally lighter compared to SWA cables, making them easier to handle and install, especially in long runs.
Electrical Characteristics
SWA Cable: The steel wire armor can sometimes affect the cable’s electrical properties, such as its inductance and capacitance.
STA Cable: The steel tape in STA cables has a minimal effect on the electrical properties of the cable.
Applications
SWA Cable: Ideal for underground systems, outdoor applications, and in places where cables are prone to mechanical damage, like construction sites.
STA Cable: More suited for buried systems, indoor applications, and where direct mechanical protection is not as critical.
Cost Implications
SWA Cable: Generally, SWA cables are more expensive than STA cables due to the higher cost of the steel wire armor.
STA Cable: STA cables are a more cost-effective solution, especially for applications where extreme mechanical protection is not necessary.
Classification of Armoured Cables
–
Armoured cables can be further classified based on the type of conductor used (copper or aluminum), insulation material (PVC, XLPE, etc.), and the presence of single or multiple cores. This classification helps in selecting the appropriate cable for specific electrical requirements.
When to Use Armoured Cable
Armoured cables are ideal in environments where the cable might be exposed to mechanical damage, such as in industrial areas, underground, or in outdoor applications. They are also used in areas prone to rodent attacks or where additional protection is required.
Advantages of Armoured Cable
–
Enhanced Protection: The armor layer provides significant protection against mechanical damage.
Longevity: Armoured cables are durable and have a longer lifespan in harsh environments.
Safety: They reduce the risk of cable-related accidents, ensuring a safer installation.
Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of applications, both indoor and outdoor.
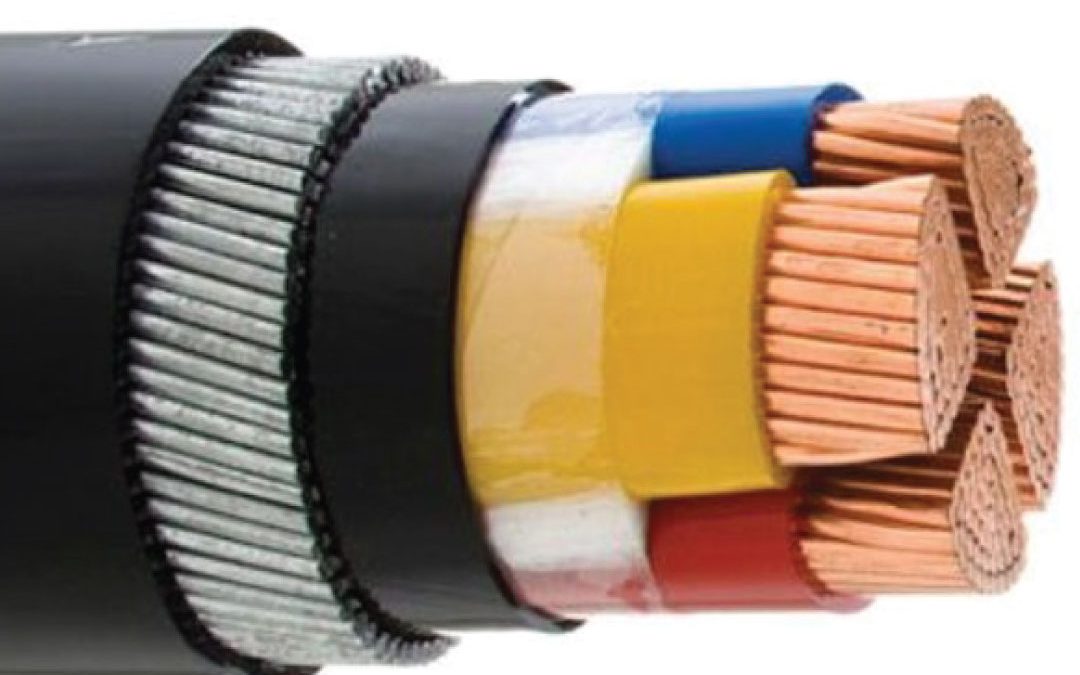
Cable Construction
1. Conductor: The conductor, typically made of copper or aluminum, carries the electrical current.
2. Insulation: This layer, made from materials like PVC or XLPE, insulates the conductor to prevent electrical leakage.
3. Bedding: This encases the insulated conductors, providing a protective layer before the armor is applied.
4. Sheath: The outer sheath offers an additional protective layer against environmental factors like moisture and chemicals.
5. Voltage Rating: Armoured cables are designed to operate at various voltage ratings, suitable for different applications.
6. Armour: The armor layer, made from materials like steel, aluminum, or wire, provides mechanical protection.
Conclusion
Armoured cables represent a crucial component of modern electrical infrastructure. Their robust construction ensures uninterrupted power supply and communication in diverse environments, from bustling industrial sites to the quiet depths underground.
Understanding the types, construction, and applications of armoured cables is essential for engineers and technicians in ensuring safe, efficient, and long-lasting electrical installations. As technology advances, the evolution of armoured cables continues, promising even greater efficiency and adaptability in the future.